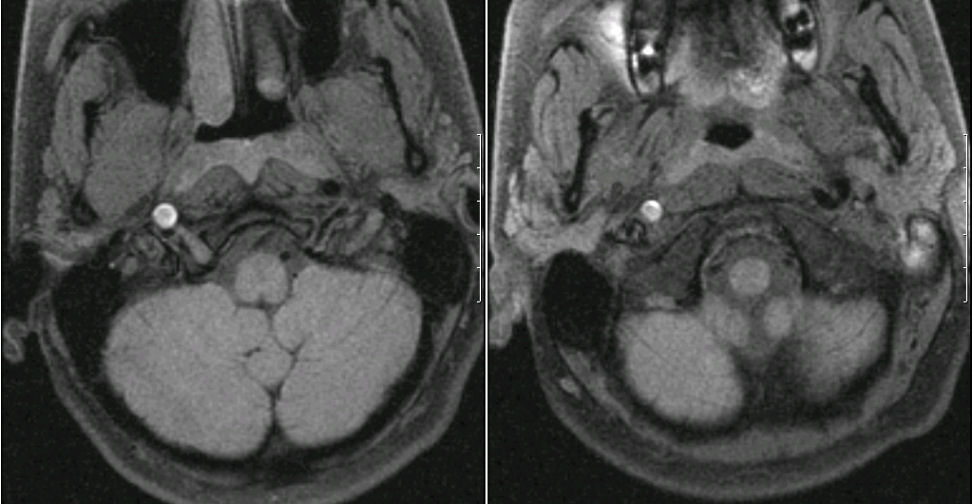
A 28 year-old woman presented with right neck pain and a right Horner's syndrome after a mild motor vehicle accident.

![]()
![]()
MRI - Axial images of the lower brainstem - fat suppression images (i.e., dissection protocol) - notice the bright signal in the right internal carotid area. The bright signal is blood, indicating a dissection of the carotid artery. During a dissection, the inner wall of the artery tears, allowing blood to enter the wall of the vessel, effectively narrowing or occluding the lumen. In the case of the carotid artery, as the sympathetic fibers run in the carotid sheath and the carotid expands from the dissection, the sympathetic fibers are disrupted resulting in the ipsilateral Horner's syndrome. The major morbidity of dissection is stasis of blood flow past the point of dissection, leading to fibrin clot, then distal embolus and stroke. Treatment with anticoagulation is most often prescribed to prevent this complication.
Revised
04/24/06.
The Electronic Curriculum is copyrighted 1998, Case Western Reserve University
School of Medicine.